Product Overview
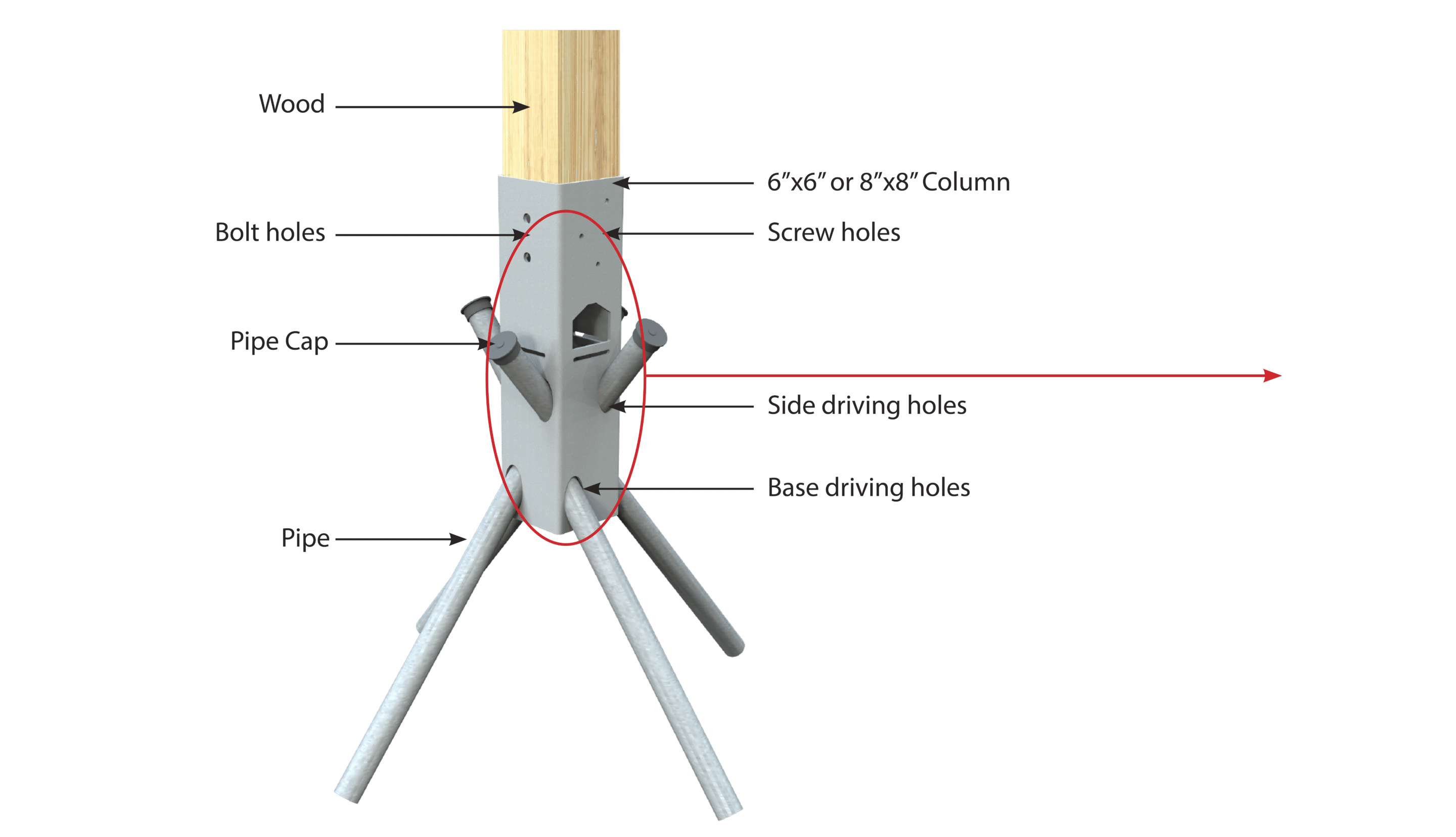
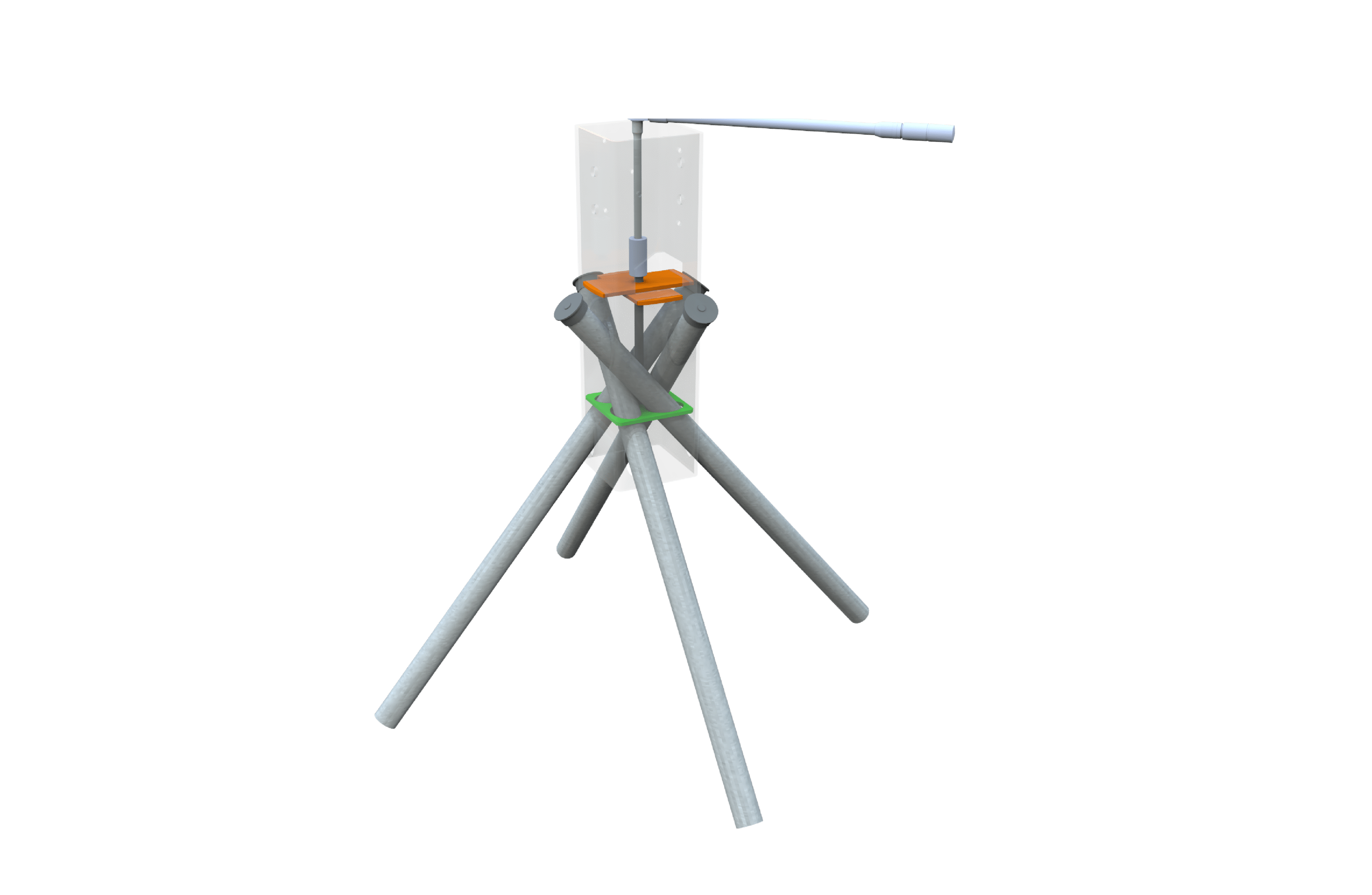
Ground Frame Column
All Ground Frame foundations are custom-engineered to meet your specific design and site conditions. If needed, Ground Frame columns can be included in your foundation system. Typically used for sloped sites, these columns offer the same high-quality engineering as beams and are available in powder-coated, galvanized, or raw steel finishes. After collaborating with our expert team and a geotechnical engineer, your components will be precisely engineered to ensure optimal performance. Ground Frame columns are versatile and can be used on both flat and sloped sites.
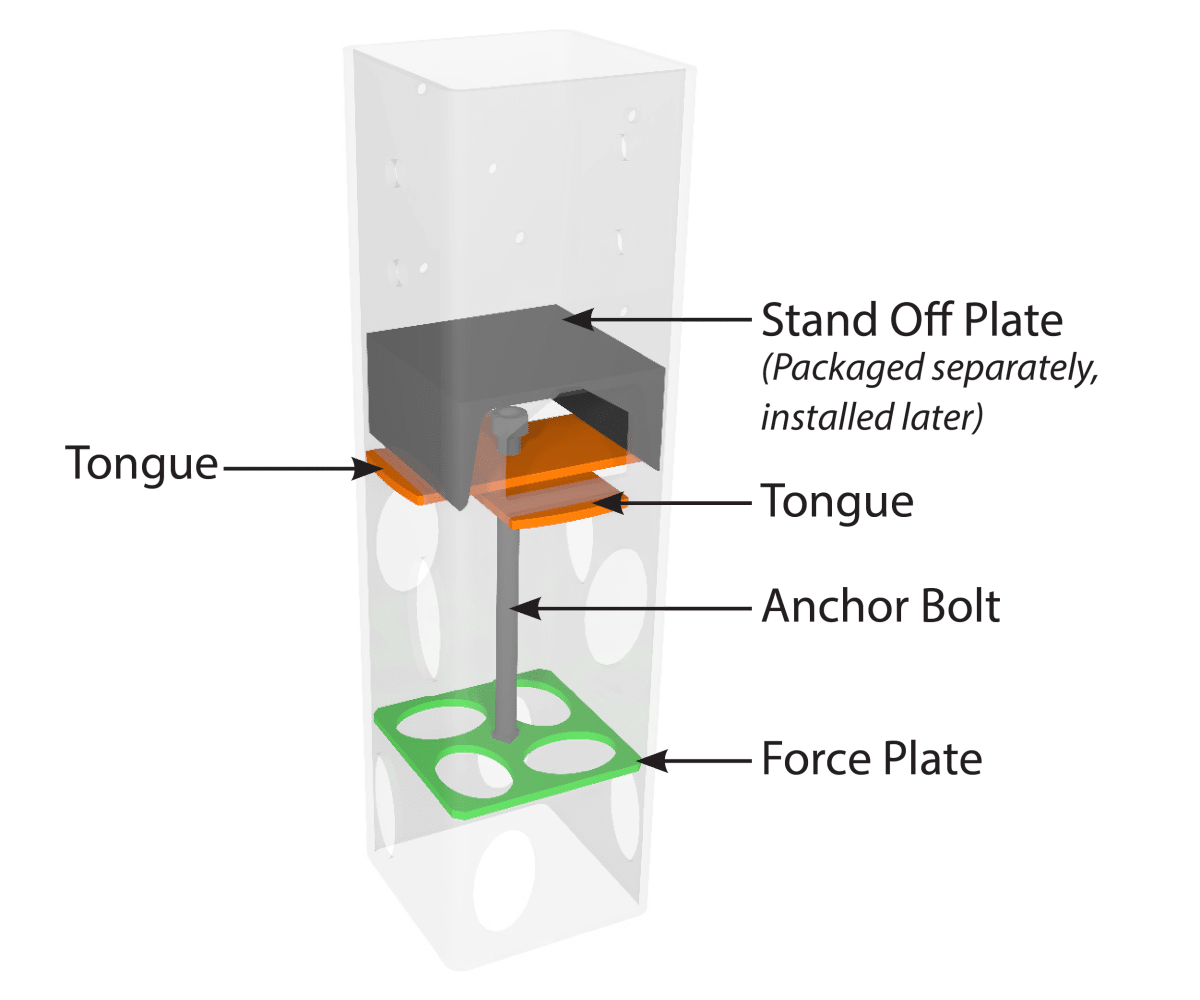
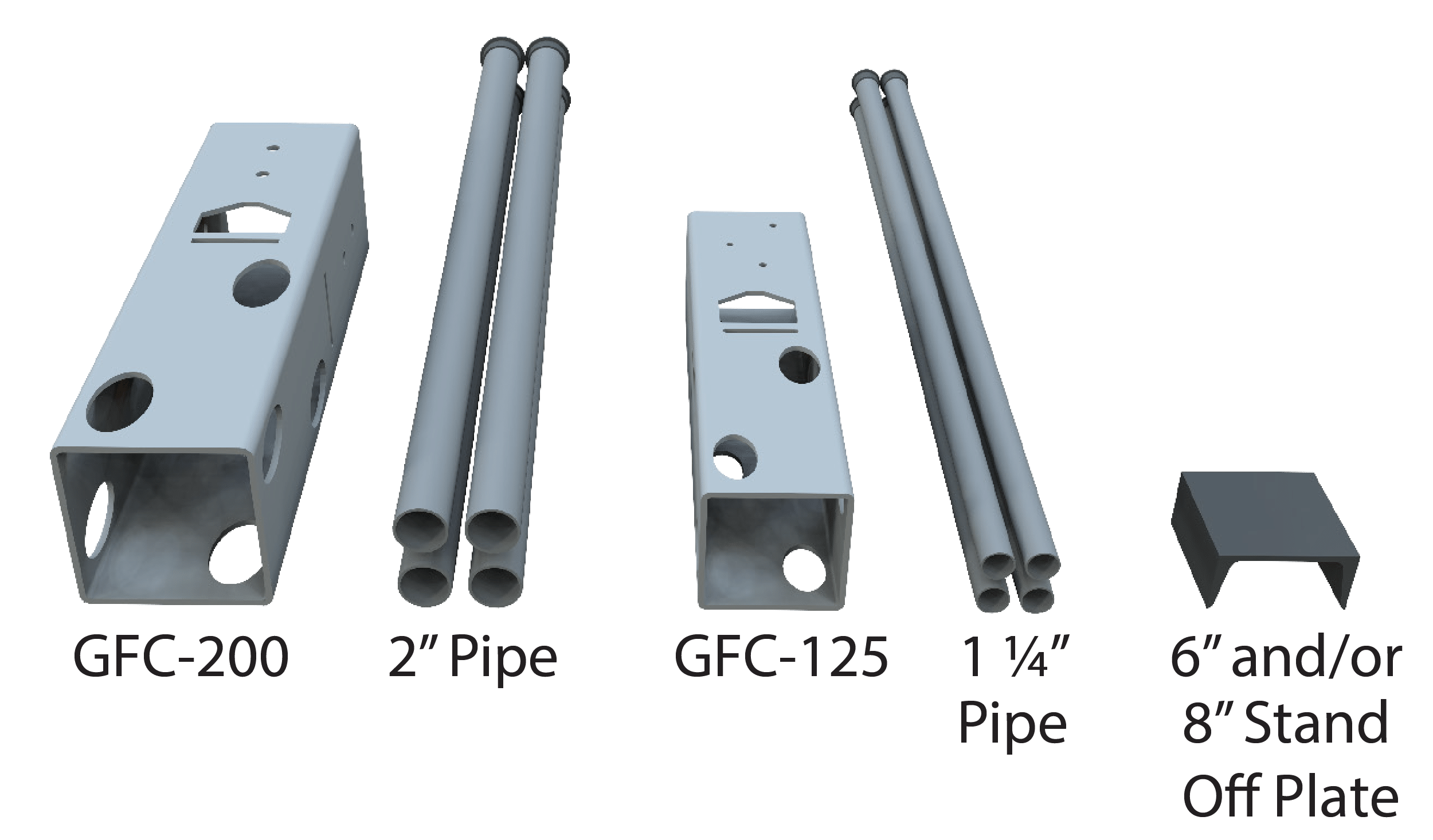
Ground Frame Smart Part Numbers
Simplify field inventory checks using out smart part numbers.


Positioned and Ready: Pipes Set for Efficient Installation
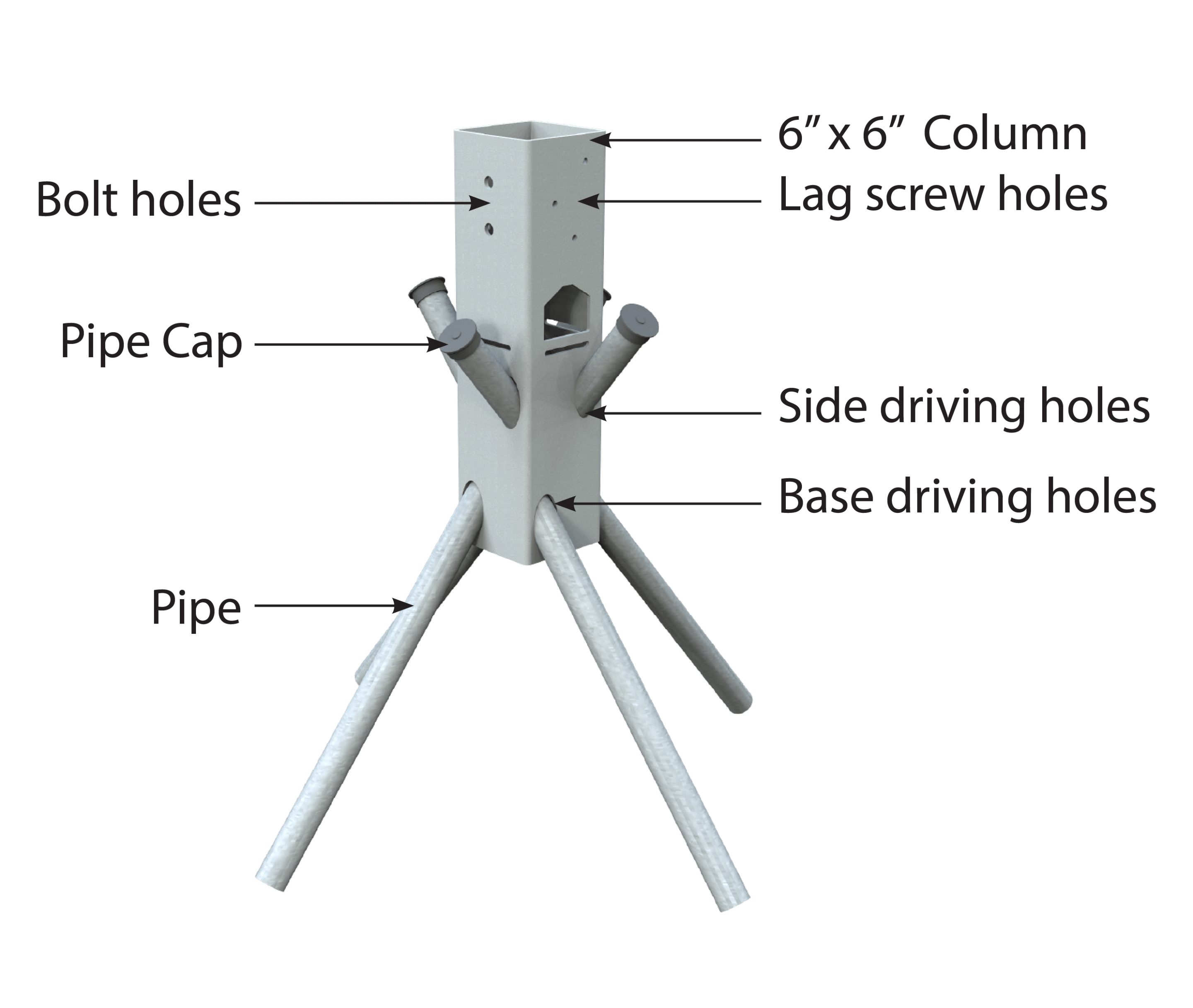
Column Installation: Core Principles
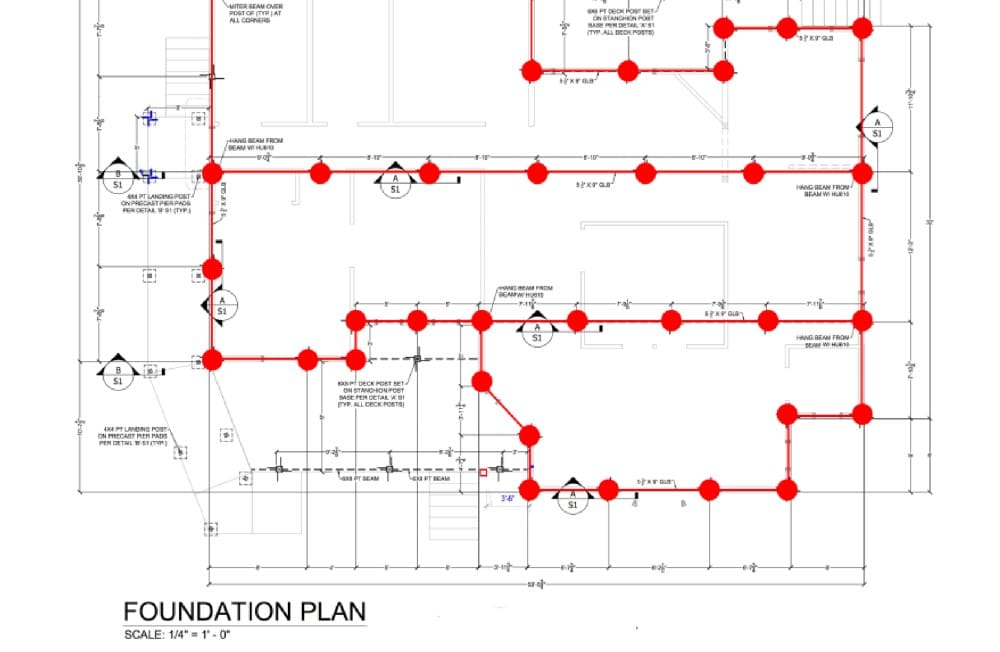
After site preparation is complete roughly stage the Ground Frame columns using approved dimensioned layout
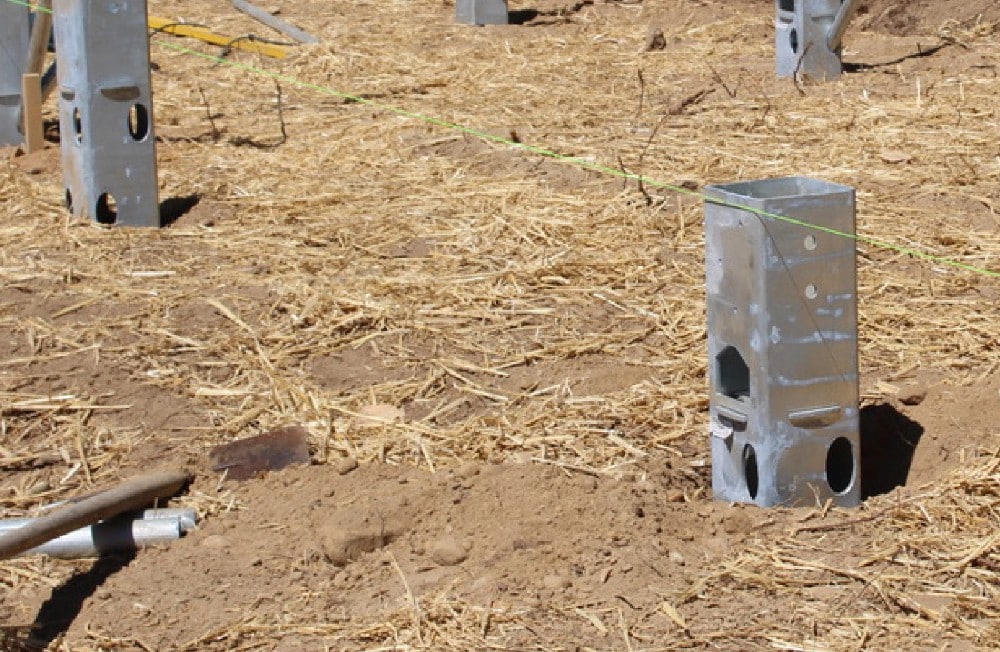

Dig a square hole and compact the soil to create a firm base, then place the column into the hole
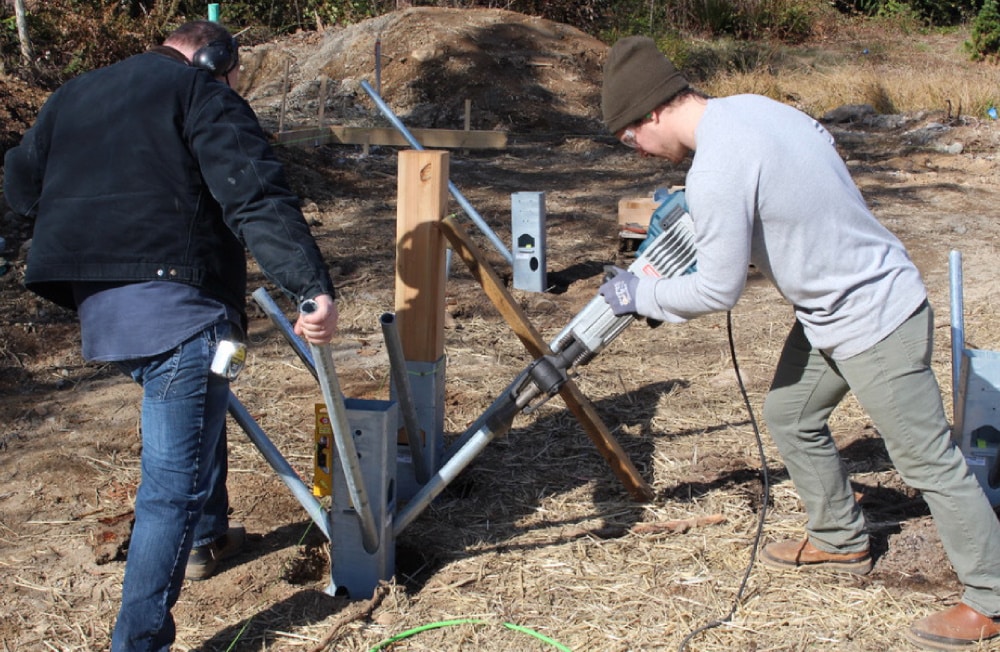

After stabilizing the pipes a few inches with a sledgehammer, drive the pipe through the side driving holes using a jackhammer

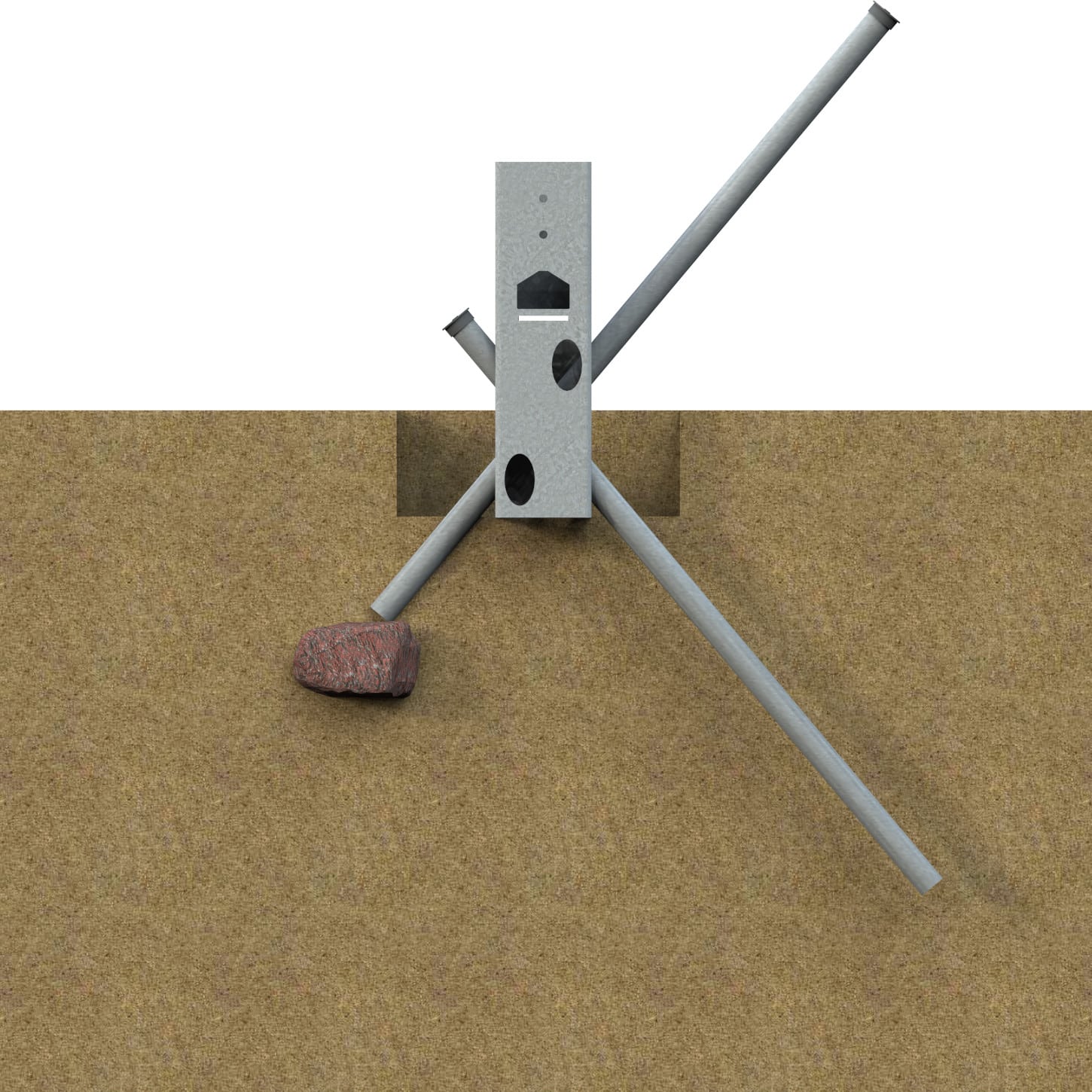
Working with Obstructions
Ground Frame pipes are designed to handle obstructions commonly found in soil. Designed for flexibility, Ground Frame pipes either be removed or field cut to navigate shallow or deep obstructions.

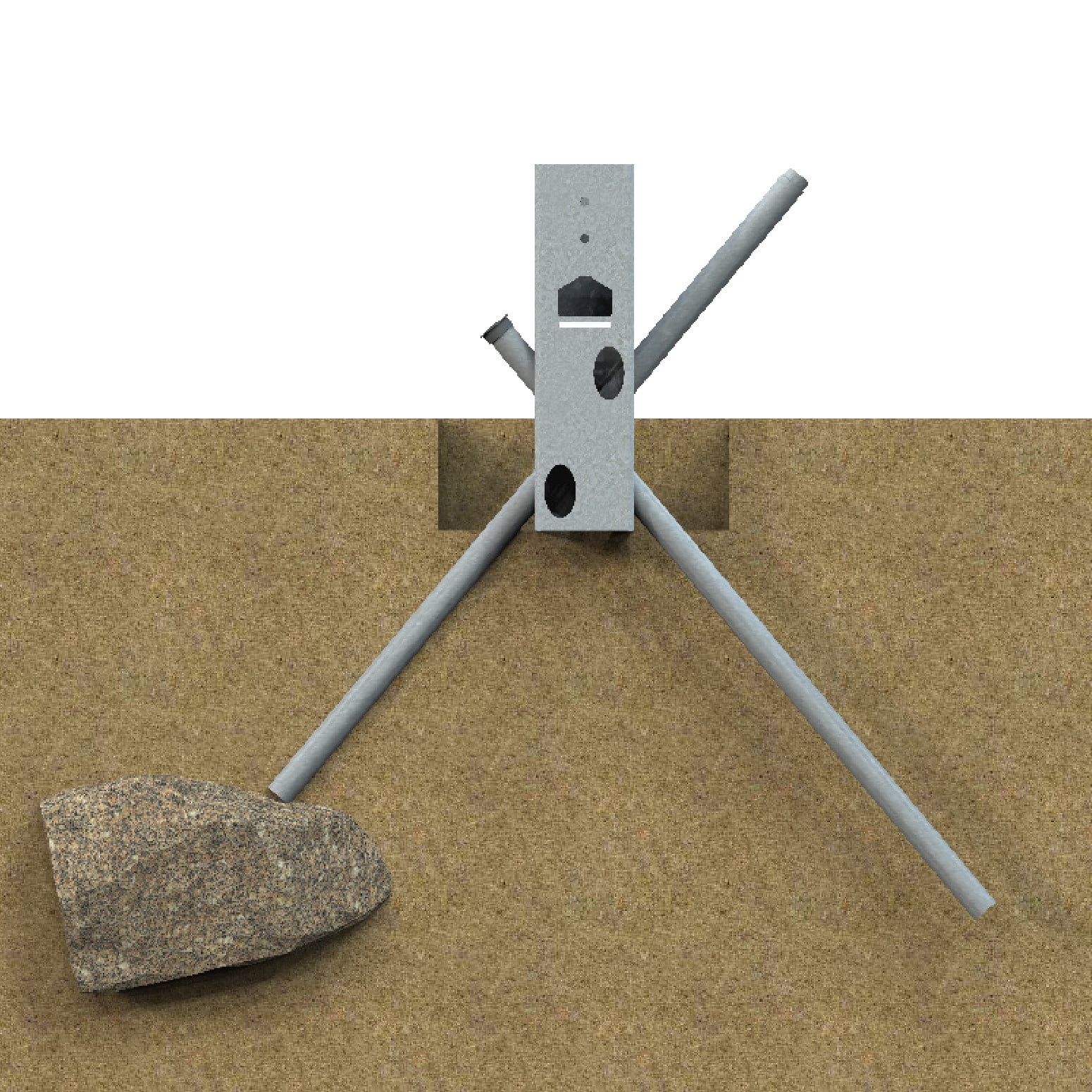
If less than 1/3 of the pipe is in the ground, remove the pipe and obstruction, recompact soil, re-drive the pipe.
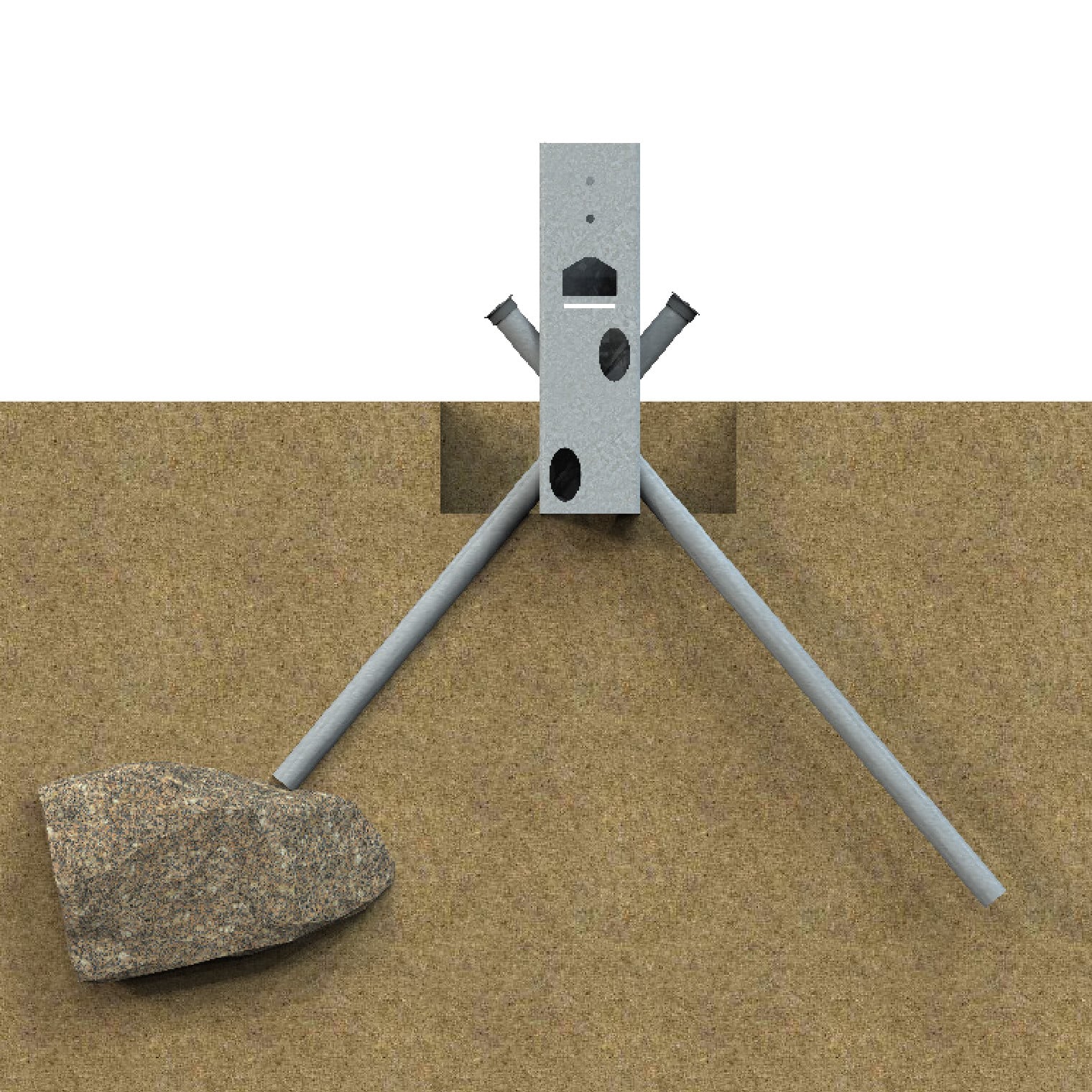


Cap the pipe and note the length of pipe removed in the driving log.

